 Image credit: Mol. Phys.
Image credit: Mol. Phys.Abstract
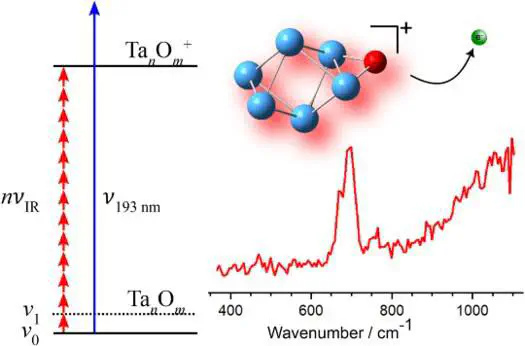
Resonant and non-resonant multiple photon excitation of small tantalum and tantalum oxide clusters, TanOm (n = 4–15, m = 0, 1, 2) is shown to lead to thermionic emission and the production of the corresponding cationic clusters. In this way, we have recorded mass-resolved photoionisation spectra in the mid-infrared using the intense free-electron laser for intracavity experiments (FELICE). All spectra exhibit a broad non-resonant band with lower thresholds around 800 cm−1 whose efficiency increases to higher wavenumbers as fewer photons are required to reach the ionisation threshold. In addition, the neutral oxide clusters have strong resonant absorptions feature assigned as the oxide symmetric stretching mode, and their infrared spectra are very similar to those reported previously for the corresponding cationic clusters, TanOm+, recorded by infrared multiple photon dissociation.